Between 28 September and 15 October 2015 the exercise Trial Embow 2015 was held at the range of WTD 91 in Meppen (Germany). This item gives some insight into the participants and purpose of the exercise.

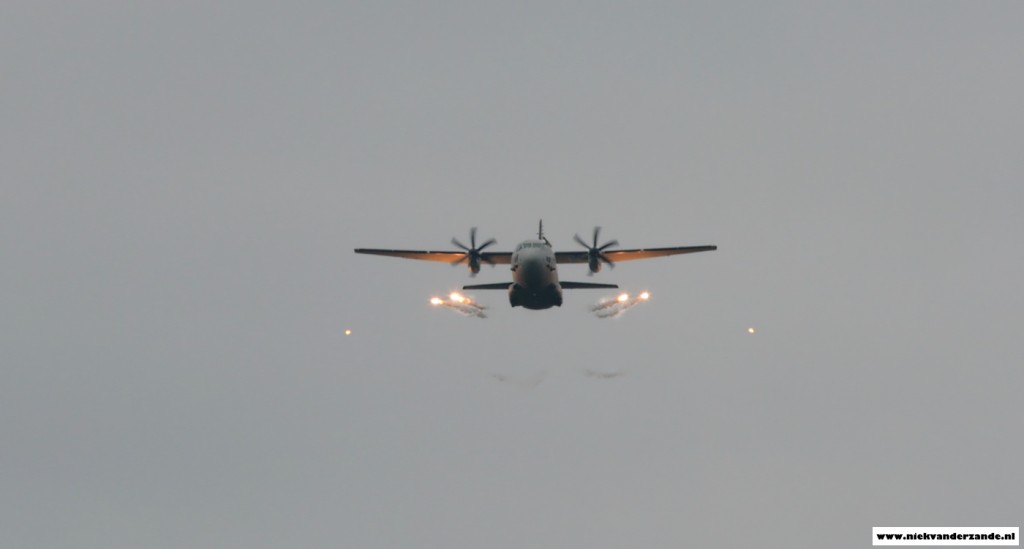
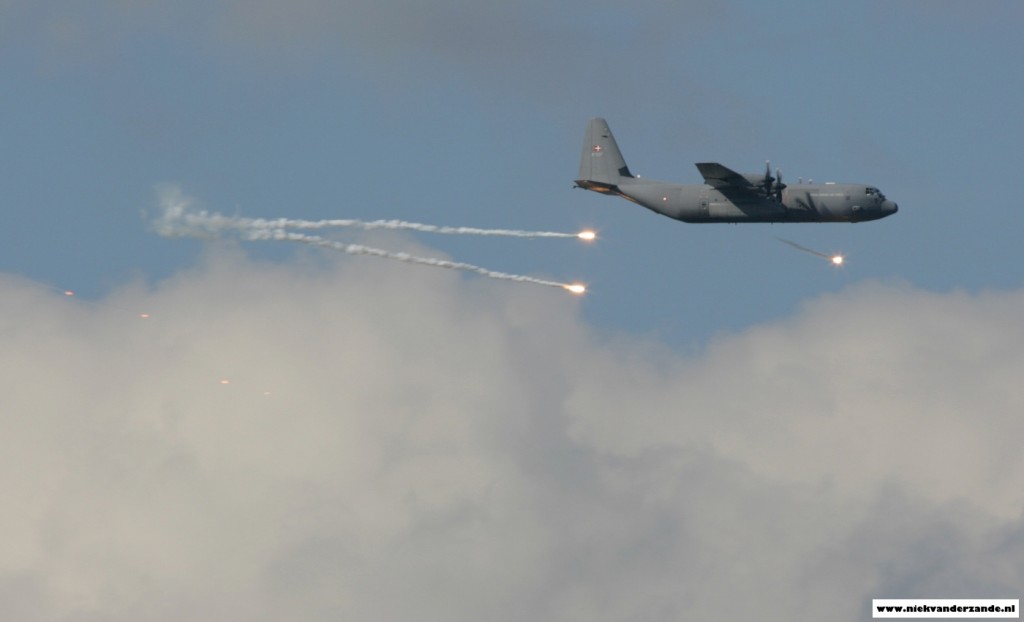
The purpose of the Embow excercises is to familiarize aircrew with the self-defence tools that they carry against ground-based systems. The main aim of Embow is to allow aviators to test, under live and monitored conditions, the capacity of their aircraft to evade infrared-guided surface-to-air missiles, from basic Manpads to more advanced surface to air short-range systems (SHORADS). As a cherry on the cake, the Embow trials are always performed in highly instrumented areas so that the participants can take a close look at the actual efficiency of the systems they field. Any noticed discrepancy is then funneled, in a second move, back to the industry for updating and improvements.

For this year’s edition the WTD 91 range was chosen as the location. The range is the largest instrumented range in Europe and with dimensions of 7 by 31 kilometers and a reserved airspace up to an altitude of 5000 feet. Next to that the facility has its own airfield and helipad, which was very useful for the helicopters participating in the exercise.
Down on the Range
During a typical sortie, the range was booked for the duration of 30 minutes. Sorties were only flown by single aircraft, as the whole mission had to be measured. The aircraft would then fly a pre-determined set of patterns (radials) upon which a flare would be dropped after a count down from the ground station. These missions were also flown with different types of flares per aircraft type. Evaluation of the measurements would then show if the flare behaved in the same way as specified by the producer.
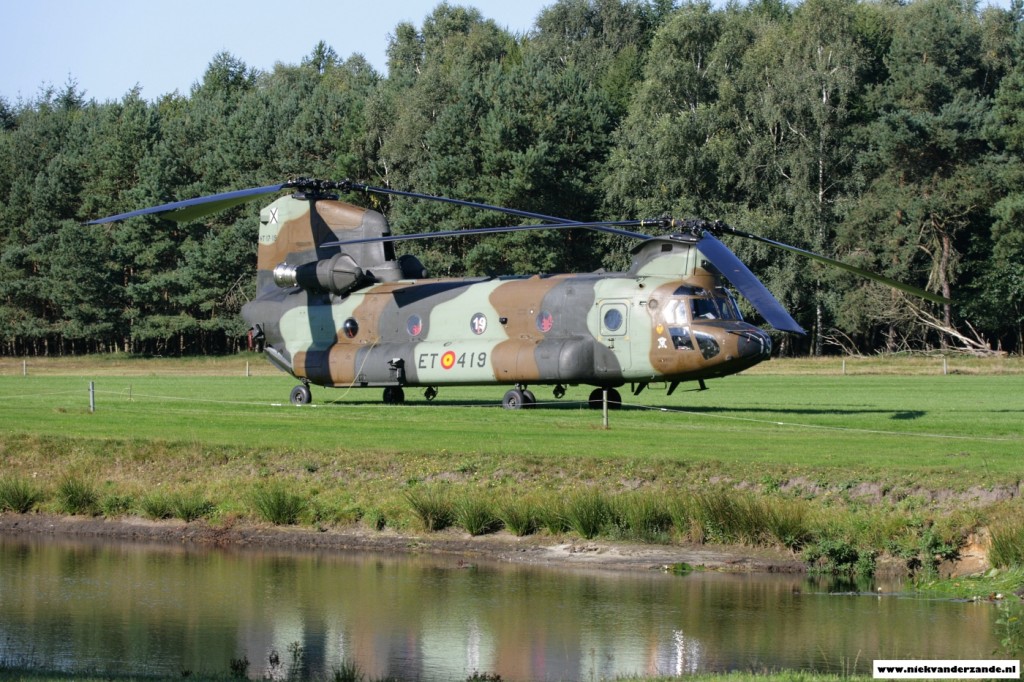

At the airfield
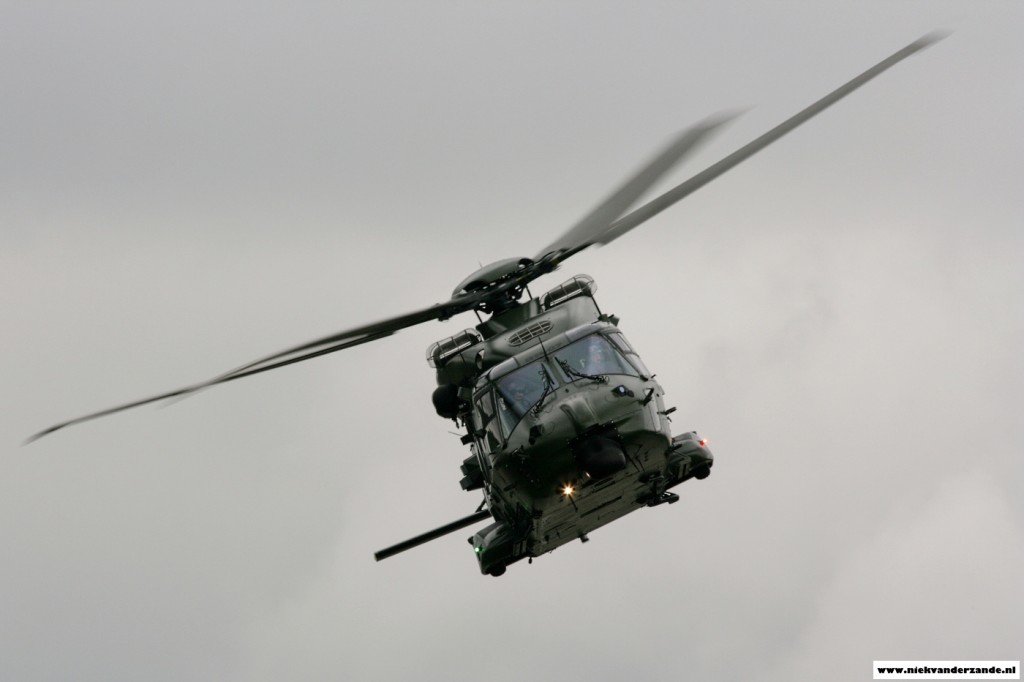
Trial Embow XV saw participation from all over Europe with various types of aircraft, ranging from a Belgian A.109 Helicopter to the British C-17 transport aircraft. Particpating countries were Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Italy, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom.
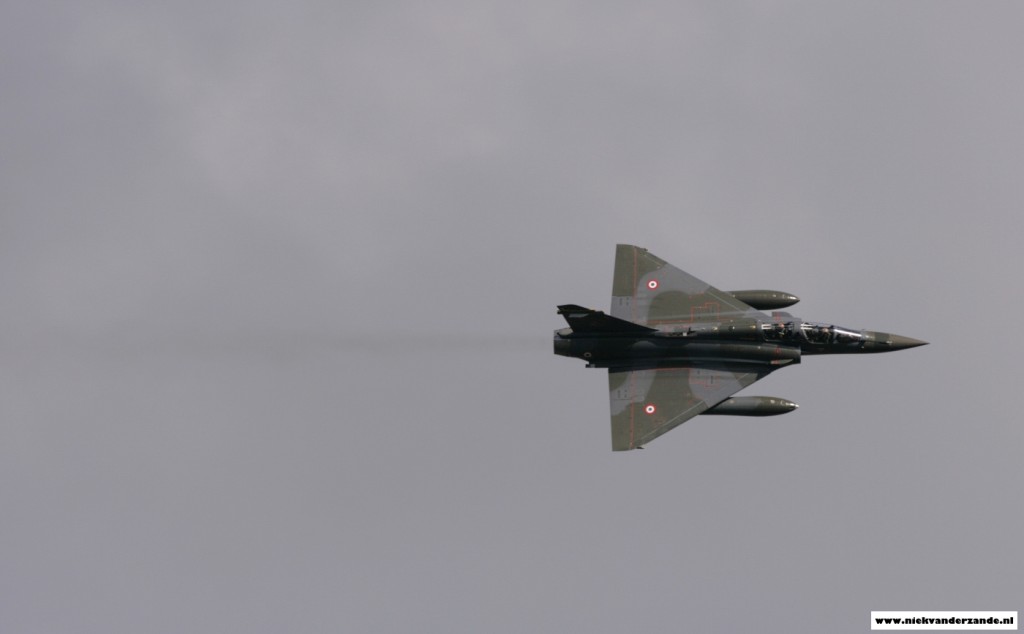

Most helicopters were temporarily based at Meppen’s airfield, whereas most fighters operated from Nörvenich and Leeuwarden airbases. Most transport aircraft flew directly form their homebase. Upon arrival at Meppen (EDR-34), they would change their normal radiocallsign to a callsign ranging from Outlaw01 to Outlaw10.






































